In the spring of last year, the media around the world circulated sensational information about the discovery of a fetus in a female mummy held at the National Museum in Warsaw. The authors of this discovery, from the Warsaw Mummy Project team, found that the woman died in the 26th–30th gestational week, i.e. at the beginning of the third trimester, and the fetus was not pulled out during embalming – contrary to the treatment of the viscera of the female, which were removed through an incision in the lower part of the abdomen. They also observed that the mummified fetus had broken bones (not shown on the published radiograph) and was found in two parts, which was interpreted as the result of the postmortem fracture of the female pelvis.
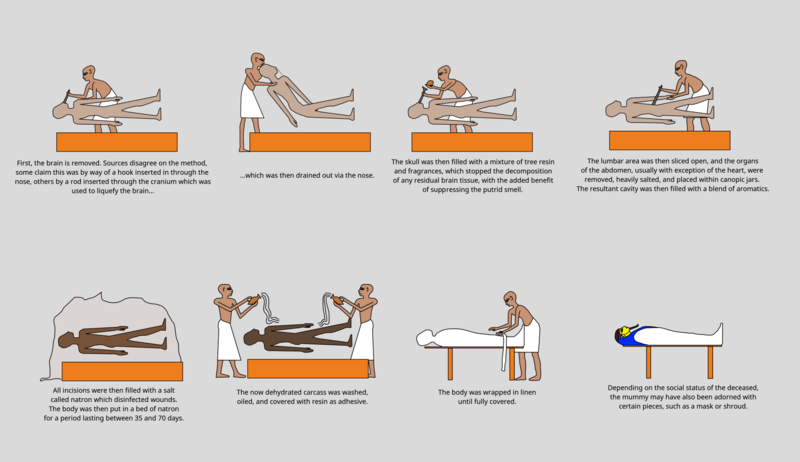
drawing by SimplisticReps, published on licence CC BY-ND 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Continue reading “The mummy with a pickled fetus: another example of wishful thinking”