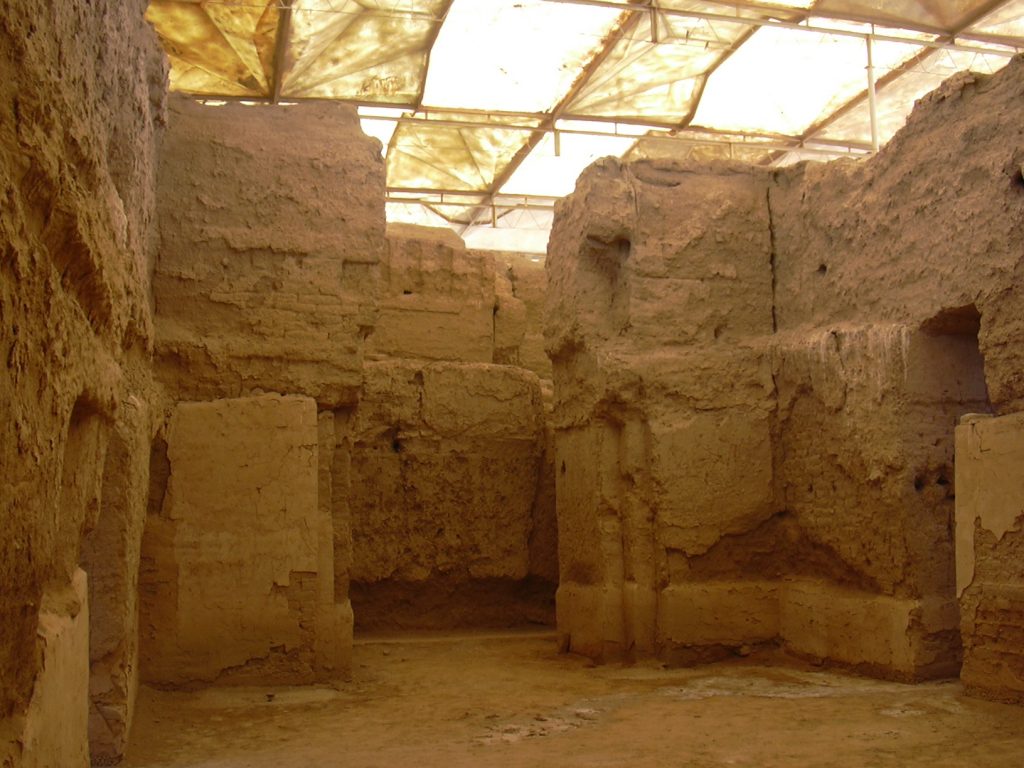
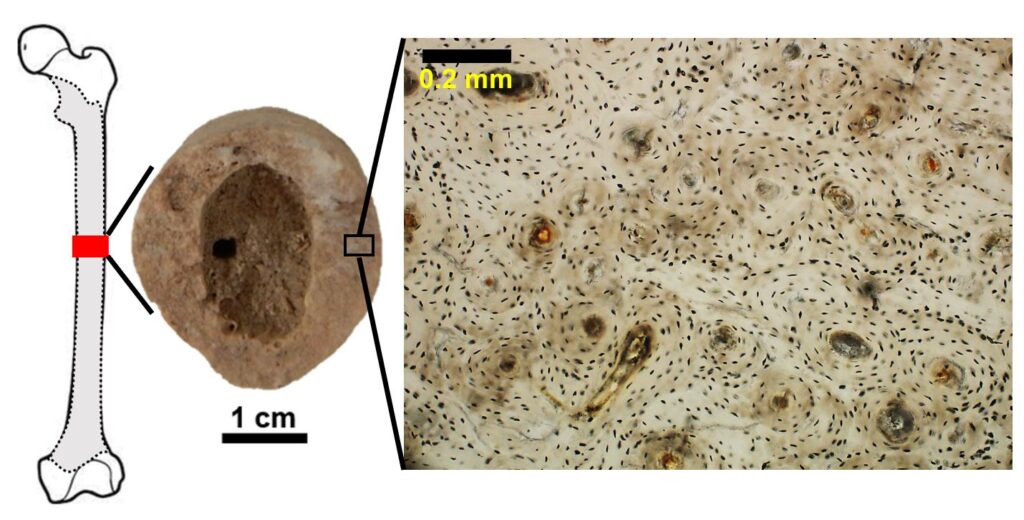
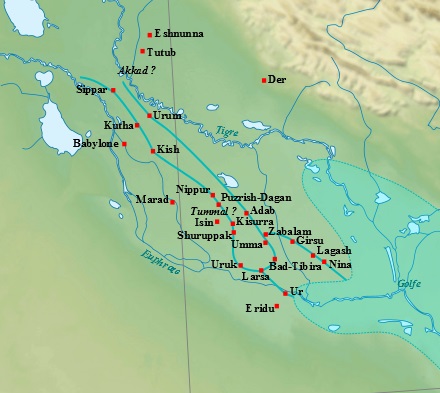
The earliest large cities emerged in northern Mesopotamia during the Late Chalcolithic (c. 4200 – 2900 BCE). It was a time of transformation from local village-based social structures to big cities with hierarchical societies, more sophisticated division of labour and development of central authorities towards early states. The process of urbanization is well indicated by the rapid increase in settlement size, which at Tell Brak reached more than 120 hectares in mid-4th millennium BCE. It was however not clear whether this process was due to local population growth or migration and absorption of people from different areas. A recent bioarchaeological study published in the Journal of Anthropological Archaeology offered a new line of evidence, suggesting that the Late Chalcolithic urban growth was supported by migration. Much like today, people migrated into the city and settled in neighborhoods based around their shared migratory origins. These neighborhoods remained distinct communities that did not begin to integrate for multiple generations.
Continue reading “Tales as old as time: Teeth reveal migrant neighborhoods in ancient Mesopotamia”