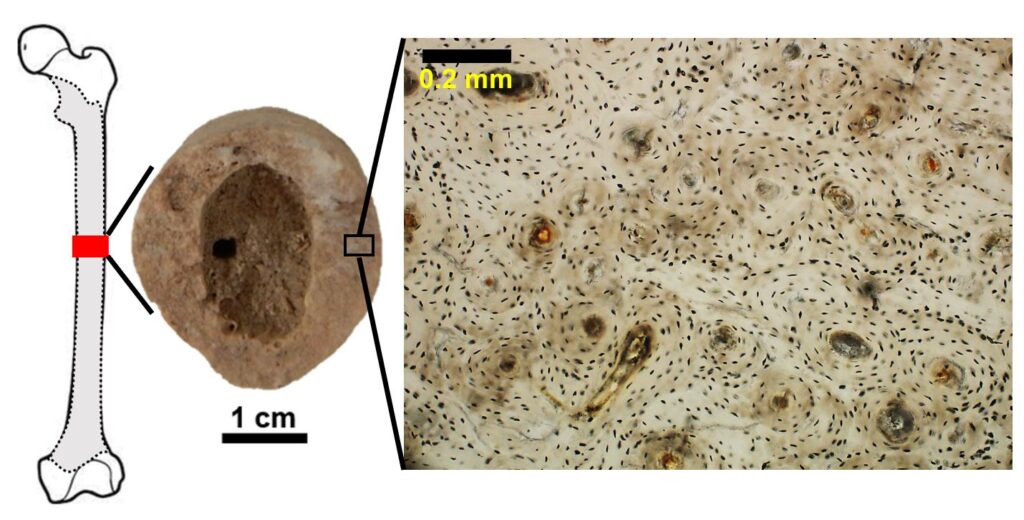
When bioarchaeologists excavate human remains, they are sometimes faced with burials that can be somewhat complicated. A ‘perfect’ burial for bioarchaeological analyses would contain a complete set of bones that are well preserved. Some archaeological sites, however, are of such great significance that we even work with poorly preserved and incomplete burials, using unconventional methods that allow us to overcome these preservation limitations. This was proven by our research team whilst studying the Bronze Age cemetery of Deh Dumen, located in the Zagros Mountains in Iran.
Continue reading “New study sheds light on the ancient pastoralists of Iran”
